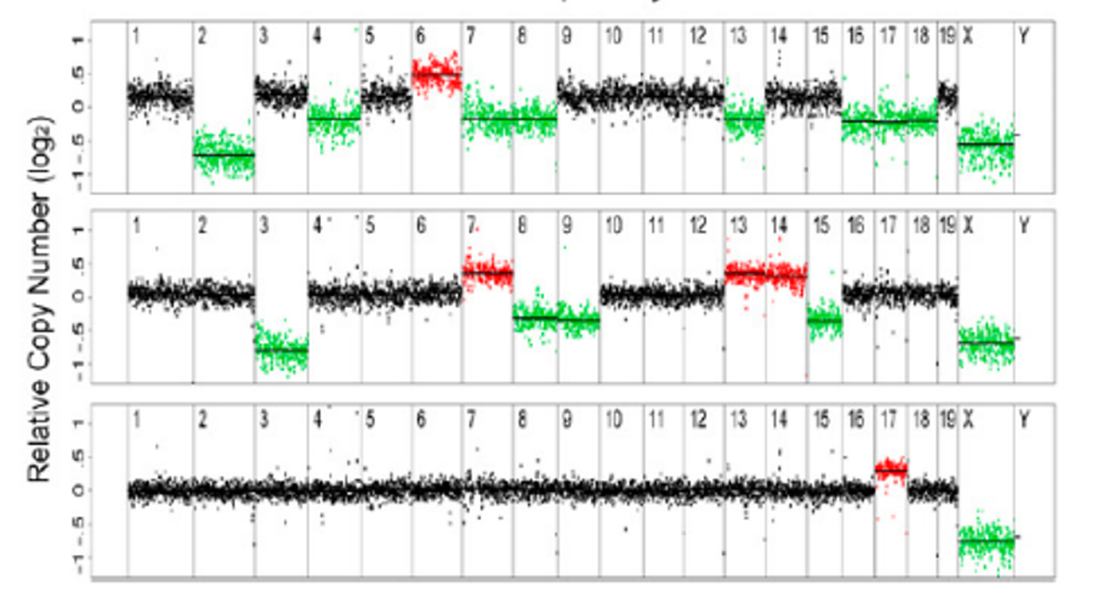
Copy Number Variants with Shallow Sequencing
While working at MIT, Kristin Knouse (Amon Lab) and I developed a workflow to reliably detect copy number variants (CNVs) from shallow whole-genome sequencing data. Our goal was to investigate previous reports of unexpectedly high levels of large-scale CNVs in somatic neural cells. Through simulations, we defined optimal parameters for CNV detection and found that, using these optimized parameters, the prevalence of large CNVs in somatic cells is lower than previously reported, which aligns better with biological expectations. This work established a standard for calling CNVs from shallow whole-genome sequencing data in single cells.
Read More
OLego, A Sensitive Splice Mapper
OLego is a program specifically designed for de novo spliced mapping of mRNA-seq reads. OLego adopts a multiple-seed-and-extend scheme and does not rely on a separate external mapper. It achieves high sensitivity of junction detection by using very small seeds (12–14 nt), efficiently mapped using the Burrows-Wheeler transform (BWT) and FM-index. This approach also makes it particularly sensitive for discovering small exons. OLego is implemented in C++ with full support for multithreading, enabling fast processing of large-scale data.
Read More
SpliceTrap, A Splicing Quantification Tool
SpliceTrap is a statistical tool for quantifying exon inclusion ratios in paired-end RNA-seq data, with broad applications in the study of alternative splicing. SpliceTrap estimates exon inclusion levels using a Bayesian inference approach. For each exon, it quantifies the extent to which it is included, skipped, or affected by size variations due to alternative 3’/5’ splice sites or intron retention. Additionally, SpliceTrap can quantify alternative splicing within a single cellular condition, without requiring a background set of reads.
Read More